Los Angeles
Los Angeles [læs ændæRayls ] (from Los Ángeles in Spanish [losa"Die Engel"), officially City of Los Angeles, often L.A. abbreviated, is the largest city in the state of California. It is located on the Pacific Ocean and Los Angeles River.
| Los Angeles | |
|---|---|
| nickname: L.A., City of Angels, City of Flowers and Sunshine, La Land, The Big Orange, Southland, El Pueblo | |
From upper left to lower right: Downtown Los Angeles, Venice, Griffith Observatory, Hollywood Sign | |
seal |  flag |
| Situation in County and California | |
| | |
| base | |
| Foundation: | September 4, 1781 |
| State: | United States |
| State: | California |
| County: | Los Angeles County |
| coordinates: | 34° 3′ N, 118° 15′ W |
| Time zone: | Pacific (UTC-8/-7) |
| inhabitants: | 3.979.576 (status: 2019) |
| population density: | 3,275.6 inhabitants per km2 |
| area: | 1,290.6 km2 (approx. 498 mi2) of which 1,214.9 km2 (approx. 469 mi2) country |
| Height: | 100 m |
| Structure: | 15 districts |
| ZIP/postal Codes: | 90001-90068, 90070-90084, 90086-90089, 90091, 90093-90097, 90099, 90101-90103, 90174, 90185, 90189 |
| area code: | +1 213, 310, 323, 424, 661, 818 |
| FIPS: | 06-44000 |
| GNIS ID: | 1662328 |
| website: | www.lacity.org |
| Mayor: | Eric Garcetti (D) |
| |
Los Angeles on the map of the United States |
Los Angeles is the second largest city in the United States, with 3,976,322 inhabitants (2016) in the city area, after New York City and before Chicago. With 11.8 million inhabitants in the agglomeration and more than 12.8 million inhabitants in the Metropolitan Statistical Area and just under 17.8 million in the enlarged metropolitan area, the Greater Los Angeles Area ranks 18th among the largest metropolitan regions in the world. position. The inhabitants of Los Angeles will become Angelenos [ændallocation.over Asia.
Los Angeles is the capital and administrative seat of Los Angeles County. The city is California’s economic, commercial and cultural center with numerous universities, universities, research institutes, theaters and museums. Los Angeles is the world's largest location for the aerospace industry and is well known for its film and television industry (Hollywood) and music scene.
In 2017, the Los Angeles metropolitan region achieved economic output of around $1.04 trillion. It ranks third among the cities in the world behind Tokyo and New York City.
Name of the city
The city was officially founded on 4 September 1781 by the Spanish Governor Felipe de Neve as El Pueblo de la Reina de Los Ángeles (the "Village of the Queen of the Angels"). The name thus referred to Mary as the Queen of the Angels, a Marientile from the Lauretanian liturgical. The current name Los Angeles is a shortening of the founding name to "the angels."
The unofficial name of El Pueblo de Nuestra Señora la Reina de los Ángeles del Río de Porciúncula was also widely used [El-eleven (18), the village of Our Lady, Queen of the Angels of the Portiuncula River, is just 1st in 18s. He refers specifically to the Basilica of Santa Maria degli Angeli in Assisi, built above the Portiuncula Chapel, where Franz von Assisi died. He was the founder of the Order of which the missionaries who came to America with the explorers were members.
Contrary to popular belief that the original name was such, scientists from official documents by Governor Felipe de Neve, Commander-in-Chief Theodor de Croix and Vice-King Antonio María de Bucareli y Ursúa have found that the settlement was simply named El Pueblo de la Reina de Los Ángeles.
The abbreviation often used (also in colloquial language) is ‘L.A.’. Because of the Spanish importance of the name of the city, the city is named the City of Angels.
geography
location
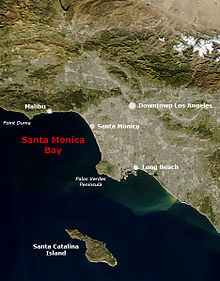
The city center and the suburbs of Los Angeles are on average 100 meters above sea level in a hilly coastal region. To the west and to the south, the city borders the bay of Santa Monica of the Pacific Ocean. In the east and north it is surrounded by mountain chains. The San Fernando Valley is also to the north of the city, where one third of the inhabitants live in single-family houses. The valley is cut off by the Griffith Park and the Santa Monica Mountains of Hollywood and the city center.
The administrative city area covers an area of 1290.6 km². Of these, 1214.9 km² are land and 75.7 km² are water. The urban area stretches 71 km in north-south direction and 47 km in east-west direction. It is connected by a system of highways made of steel and concrete structures. The city is burdened by the world's largest density of cars, and car and industrial emissions have become a pressing environmental problem. That's why Los Angeles is one of the cities with the greatest smog burden in the United States.
The city is sometimes called a horizontal city because it has relatively few skyscrapers and the entire city area is very large. However, high land prices in the center of Los Angeles mean that high-rise buildings are gaining ground there. The agglomeration, which is the continuously built area, covers an area of 4320 km².
There are various definitions of the metropolitan area of Los Angeles:
- The Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) comprises the 15 districts of Los Angeles and the two counties of Los Angeles (Metropolitan Division Los Angeles-Long Beach-Glendale) and Orange (Metropolitan Division Riverside-San Bernardino-Ontario). It has a floor area of 12,562 km².
- The Combined Statistical Area (CSA) comprises 173 independent cities. It includes the counties of Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside, Ventura and Orange. The enlarged metropolitan area thus extends to the border of Nevada and covers an area of 87,941 km². Only a fraction of this land is used for urban development. Most of it is uninhabited, the Mojave Desert and the Joshua Tree National Park, located in Riverside and San Bernardino County.
geology
San Andreas's fault runs along the eastern beach of the metropolitan area; The Puente Hills defense is located just below the city. The resulting earthquake risk explains the strict construction rules applied throughout the South California earthquake zone. Since 1800, nine major earthquakes have struck Los Angeles, with a magnitude of six and more and thousands of smaller earthquakes. Numerous buildings are earthquake-proof, which significantly reduces the number of earthquake deaths.
Until 1958, there was also a legal requirement that the building ceiling should not exceed 45 meters and 14 floors, respectively. One exception was the town hall of 1928 at 138 meters. Earthquake-proof constructions made the law redundant later. The threat of earthquakes, the abandonment of dense construction, and the establishment of a narrative that Los Angeles should rather become a "city in the Garden" were the ideas behind this rule. Again, this is an explanation for the extension of the city.
The most severe earthquake in recent history was the Fort Tejon earthquake on 9 March 2006. January 1857, near the present municipalities of Wrightwood and Palmdale. The magnitude 7.9 earthquake caused only minor damage, as the region was sparsely populated at that time. If such a quake were to occur today, the damage would amount to several billion dollars, and the loss of life would be significant.
On March 10, 1933, the long beach earthquake caused 6.4 120 deaths. In Long Beach and other places, damage of property totaled $50 million. Many of the damaged buildings were not earthquake-proof. Another major earthquake occurred on 9 March. February 1971 with a strength of 6.6. The San Fernando earthquake of 1971 (including the Sylmar earthquake) caused $500 million in damage in the San Fernando Valley and claimed 65 lives. The earthquake on the 28th June 1991 had a thickness of 5.8, but due to its depth did not cause any surface rupture. However, damages totaling USD 40 million were caused, especially in the San Gabriel Valley.
On January 17, 1994, a magnitude 6.7 earthquake struck the city of Los Angeles. The epicenter of the Northridge earthquake was in the Reseda district in San Fernando Valley. 57 people died and 12,000 were injured. Major transport links and an estimated 100,000 buildings have been damaged or destroyed. According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), USD 40 billion of property damage was caused.
In 2008, the US Geological Service (USGS) and the South California Earthquake Center published a new study. The researchers predicted that a major earthquake of magnitude 6.7 would occur in California by 2038, with a 99.7% probability. A quake of 7.5 or more was predicted with a 46% probability. The Greater Los Angeles area is somewhat more vulnerable than San Francisco in the north of the state. For example, a 6.7-magnitude quest in Los Angeles is 67% and 63% in San Francisco.
On 29 July 2008, an earthquake of magnitude 5.4 was registered at 11:42 local time. The epicenter was located about 46 km east-south-east from the city center, near Chino Hills.
city
Los Angeles is divided into 15 districts. The population figures refer to the census of 1 April 2000.
| district | surface in km² | resident number | resident per km² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st District | 36.17 | 236,344 | 6,534 |
| 2nd District | 130.64 | 258,603 | 1,980 |
| 3rd District | 107.54 | 258,788 | 2,406 |
| 4th District | 78.00 | 252,787 | 3,241 |
| 5th District | 122.72 | 258,749 | 4,106 |
| 6th District | 63.02 | 235,885 | 3,743 |
| 7th District | 78.09 | 235,869 | 3,020 |
| 8th District | 46.35 | 243,108 | 5,245 |
| 9th District | 38.09 | 236,932 | 6,220 |
| 10th District | 35.19 | 243,664 | 6,924 |
| 11th District | 167.68 | 258,433 | 1,541 |
| 12th District | 161.31 | 242,361 | 1,502 |
| 13th District | 34.01 | 244,369 | 7,185 |
| 14th District | 59.43 | 235,036 | 3,955 |
| 15th District | 99.74 | 253,884 | 2,545 |
| Los Angeles | 1,257.97 | 3,694,813 | 2,937 |
settlement
The Los Angeles region is characterized by extreme urban sprawl. The entire city is mosaically disbanded into a variety of individual city districts. The districts have different functions, such as business districts or residential districts, and are very different. In the individual districts there are population groups which also differ significantly in terms of origin, education, income or age structure. The districts are isolated from one another, and often even isolated by walls or fences. There is no dominant center in the entire city. The downtown Los Angeles has the only collection of skyscrapers in the huge sea of houses and is also symbolic, but is only one of many districts. Within the agglomeration of Los Angeles there are many districts with their own center, character and specialized functions, such as Long Beach, Santa Ana, Anaheim or Pasadena.
This diversification and fragmentation is a problem on the one hand, but may also be one of the reasons for the rise of the city. Los Angeles is one of the most heterogeneous cities in the world, characterized by the individualism of its inhabitants. Different environments and lifestyles co-exist, which means that urban space can no longer be seen as a coherent entity. This is reflected in the lack of a clearly visible center. Since the end of the 20th century, a number of new concepts have been developed for these post-modernist forms of settlement, such as Exopolis, Postmetropolis or the term of the intermediate city. Often these cities are also referred to as Edgeless Cities or Edge Cities, as suburban, post-urban or urban spaces. The term of the Stadtlandhybriden is an attempt to take account of developments in post-modern forms of settlement, with a focus on Los Angeles. Such agglomerations represent a new type of spatial development, "the prerequisite of which is extensive suburbanization." Research into these developments was focused on the research group of the Los Angeles School of Urbanism, especially in the late 1980's and 1990's.
climate
The city is located in the subtropical climate zone. The average annual temperature is 18 degrees Celsius and the average annual rainfall is 305 millimeters. The warmest months are July and August with an average of 22.8 degrees Celsius and the coldest in January with an average of 13.2 degrees Celsius. Almost all of the annual rainfall falls occur between November and March, so it is mostly dry between May and October.
In summer, the temperatures in Los Angeles are usually around 22 to 25 degrees Celsius during the day. Without the location on the Pacific coast, it would be even warmer, as the wind from the sea will lower temperatures. In winter, however, it is slightly colder, with temperatures almost never falling below 15 degrees Celsius. At night, the average temperature drops by about 10 degrees Celsius. The humidity is between 50 and 75 percent.
The climate in the Los Angeles region is also characterized by a number of relatively distinct smaller climatic zones. This is mainly due to the various mountain ranges that separate the Los Angeles Basin from, for example, San Fernando Valley and other inland areas. In San Fernando Valley, for example, it is often several degrees warmer in summer than on the coast, while in winter it is noticeably cooler.
Every two to three years heat waves occur, with temperatures rising above 40 degrees Celsius. This is due to the so-called Santa Ana winds, which come from the deserts located to the east of the city over the Santa Ana mountains. Extensive forest and bush fires continue to occur. 3. In October 1933, 29 firemen died in the Griffith Park in one of the worst bush fires in the United States. Between late October and early November 1993, fires destroyed thousands of hectares of cultivated land in the Los Angeles area. The highest temperature was measured on July 22, 2006 in Woodland Hills at 48.3 degrees Celsius, the lowest temperature at 6. February 1989 in Canoga Park with -7.8 degrees Celsius.
| Los Angeles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monthly average temperatures and rainfall for Los Angeles
Source: ; weather account.de | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
environmental problems
The great air pollution - high levels of ozone, nitrogen oxide, and hydrocarbons - in Los Angeles, caused by local industries and automobile traffic, is a source of concern. In 2007, the Greater Los Angeles/Long Beach/Riverside was ranked among the most polluted urban areas in the United States, according to a report by the American Lung Association. In addition to the industries and everyday traffic of private cars and trucks, air pollution can be attributed to a significant part of inland transport, i.e. (h) trucks carrying goods between the quay and the shelf, often with engines idling. The aim is to remedy the situation of electric heavy goods vehicles introduced since 2009.
Pollutant concentrations are highest, especially in morning and evening traffic. The photochemical smog, the main component of which is ozone, reaches its highest concentration at noon. As the city is surrounded by mountain chains, air exchange with the surrounding countryside is blocked. The sea wind only reaches the Los Angeles basin without breaking the inversion weather over the city.
Ozone and other chemicals cause cough, eye irritation, headache and pulmonary dysfunction in the population. Efforts have been made to resolve the problem since the early 1980s. In 1979, for example, pollution levels were increased at 120 days a year, and in 1996 - after the introduction of catalytic converters - they were only measured on seven days. In the new millennium, the number of smog days has dropped to almost zero. Nevertheless, Greater Los Angeles still releases one of the largest quantities of toxic gases into the atmosphere in the country. The main reason for this is the low level of public transport.
Air pollution in Los Angeles also endangers the farther mountain lakes and snow-capped regions of Sierra Nevada and is responsible for the forest deaths. Heavy winds carry the pollutants to Palm Springs in Riverside County, where they lead to higher concentrations of pollutants.
story
foundation
The first European in the region was the discoverer Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo, who claimed the land for Spain in 1542, but did not establish a settlement. In 1771, the Spanish monks of the Order of Franciscans founded the mission "San Gabriel" near Whittier Narrows, which later formed the starting point for the settlement of the region. The Spanish missions in California were supposed to increase Spain's influence and the Church's power. In order to protect them from attacks by the indigenous people living there, the mission was fortified by a fort.
After the mission had established, the Spanish Governor of California, Felipe de Neve, sent 11 families to build the country. On September 4, 1781, the municipality of Los Angeles was founded with 44 settlers in the area of the Tongva indigenous population. At that time, the main livestock farming activity was carried out there. In the following decades, the first US settlers established themselves in the region.
In 1821, Los Angeles fell to Mexico, which gained independence from Spain after a long war. In 1835, the settlement was raised from the Mexican Congress to the city and, at the same time, to the capital of Mexico's northernmost region, Alta California. However, the second part of the decree was never enforced and was soon revised. Monterey remained the capital of California until 1849. The population of Los Angeles grew to 2,228 inhabitants until 1836, and then fell temporarily. By the mid-nineteenth century, Los Angeles was a Mexican community, but it comprised predominantly American settlers, poor Chinese workers, and a few wealthy Mexican landowners.
In 1846, William Ide proclaimed California's independence. The Republic lasted only a short time. During the Mexican-American War between 1846 and 1848, US soldiers occupied Alta California and, with it, Los Angeles, and joined the US. In 1848, it was found north of Sacramento Gold, which triggered the famous gold rush. Many gold seekers came to the region, which Los Angeles also benefited from by selling meat, fruit, and vegetables to Digger.
Shortly afterwards, the first of two European pharmacists (both of German descent) arrived in Los Angeles. The first was the pharmacist Theodore Wollweber. In 1861 Adolph Junge settled as second pharmacist. He operated his "Drug Store" at the Temple Block on Main Street for about 20 years. The German pharmacist F. J. In 1874, Gieze worked as an employee at Junge. Junges recipe book and its estate are now in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles.
industrialization
The town was given on 4th 18 April 1850, the U.S. City Law under the founding of the State of California by the U.S.; It had 1,610 inhabitants at the time. Los Angeles remained almost untouched by the secessionist war (1861-1865) between the southern states that left the United States - the Confederal - and the northern states that remained in the Union.
Floods in 1861/62 and a subsequent devastating drought have ruined many livestock farms. At the same time, a new upswing began, mainly due to land speculation. The result was an increase in land prices and the influx of many Chinese, Japanese, and European immigrants.
The rejection of Chinese migrants by large segments of the US population increased to an anti-Chinese hysteria during the economic crisis of the 1870's. On October 24, 1871, a racist uprising occurred in Los Angeles, after a war between rival Chinese gangs accidentally killed a white man. In the course of the uprising, a mob of more than 500 people of European origin fell into Chinatown and killed 19 of the inhabitants. Among those killed, only one was involved in the original gang war. In addition, a white man had been killed who had tried to prevent the murder.
The largest group of immigrants came from the Middle West, from states like Iowa and Indiana, and replaced the old Mexican elite as a new political class. Soon the old big farms were parceled and the population grew. From 1870 to 1900 the population of the city increased from almost 6,000 to about 102,000 inhabitants. In the first ten years of the twentieth century, the population was even more than tripled (1910: 319,000 inhabitants). This enormous growth was also supported by large-scale consortia, including the cities of Wilmington and San Pedro (both in 1909) in the south and Hollywood (in 1910) in the west. From 1899 to 1914, the port of Los Angeles was built in San Pedro. In 1915, the area became the largest borderline when most of the San Fernando Valley Los Angeles was joined.
The railways should prove to be an important engine of development for the next few decades. In 1869, the first railway line was opened in Los Angeles. It ran over 34 kilometers from today's city center to the then independent San Pedro, where today the port of Los Angeles is located. But it was only after the Union Pacific Railroad (San Francisco) in 1876, and the Santa Fe railway line in 1885, that connections with the rest of the country, that the city's growth accelerated. At that time, new irrigation techniques were tested and crops suitable for the region, such as: B. orange. The city soon became a synonym for good health, a clean environment, plentiful sunshine and endless citrus plantations in the eastern cities of the USA. The two competing railway lines soon undercut each other with low fares for tickets from the East Coast, helping to attract settlers to Los Angeles.
Coal was extracted from 1890 onwards. However, the substantial oil stocks under the city, which were first provided near the current Dodger Stadium in 1892, proved to be far more important for the future development. From then on, the drilling towers spread in large parts of the region in a short period of time. In the first half of the twentieth century, Los Angeles became one of the most important centers of oil production, and in 1923, a quarter of the world's output was produced in the Los Angeles region. Oil production still plays a role today.
In order to ensure the enormous growth for the future, the city's leaders in the years before the turn of the century were concerned about Los Angeles's water supply. For a city in a semi-dry climate zone, this was and remains a hugely important issue. Until then, the nearby Los Angeles River provided Los Angeles with drinking and drinking water. In 1913, when its water supplies were no longer sufficient, the first Los Angeles aqueduct was built in the north, carrying water from Owens Valley, 300 kilometers away, to Los Angeles. With the cheap supply of drinking water, Los Angeles was able in the years before and after 1910 to congregate numerous surrounding communities, including Wilmington, San Pedro (both in 1909) and Hollywood (1910).
In 1910, film producers discovered the Los Angeles region as an ideal production site and moved from New York and Chicago to Hollywood. In the following years, Gilbert M. Anderson and his Western and Mack Sennett with their slapstick comedies achieved great success worldwide. In 1927, when the film Jazz Singer helped the film to break through, a revival began. The Hollywood-based film industry became one of the most important industries in the United States and attracted many newcomers to Los Angeles. The first film of the monument in color — David O. Selznick's film Blown by the Wind - came to cinemas in 1939 and won ten Oscars.
In the 1920's, many other neighboring municipalities such as Sawtelle (1922), Hyde Park (1923), Eagle Rock (1923), Venice (1925), Watts (1926), Barnes City (1926) were also formed 7) and Tujunga (1932). Santa Monica and Beverly Hills, considered economically and culturally part of Los Angeles, have managed to maintain their autonomy to this day.
One of the most important events of the 1930s is certainly the 1932 Olympic Games. For the first time in the history of the Games an Olympic village was built for the male participants. Today the village is part of the Baldwin Hills district. The same year, Los Angeles's population rose to more than a million.
economic center
In the middle of the 20th century, the small suburban house with swimming pool and double garage had become a permanent symbol of the city. During the Second World War, a major upswing took place in the aerospace industry, which, due to war, settled in large numbers in the greater Los Angeles area.
Many German-speaking cultural workers and intellectuals chose Los Angeles as a refuge before the Nazis. These included Bertolt Brecht, Marlene Dietrich, Lion Fwwwanger, Otto Klemperer, Fritz Lang, Ernst Lubitsch, Heinrich Mann, Thomas Mann, Luise Rainer and Billy Wilder. But artists from other countries also found a new home here. Luis Buñuel, Jean Renoir, Igor Strawinsky, Arturo Toscanini and many others. Numerous great works by poets, conductors, directors and painters were created in exile; The immigrants made the Los Angeles of the 1940s a living center of European culture.
But the city also continued to struggle with racist violence. In 1943, a series of riots erupted into history as Zoot Suit Riots. They flared between the soldiers stationed in the city and the Mexican-American youth gangs, led by so-called Pachucos, who were known for the Zoot Suits they were wearing.
Already in the 1920s, despite a powerful tram network, the automobile had developed into the preferred means of transport for the Angelenos. For example, in this decade, Los Angeles had more cars relative to its population than any other American city. 1. The Arroyo Seco Parkway was opened in January 1940, the first city motorway between Pasadena and the northern city center. This marked the course for further development. After the war, companies like General Motors, Greyhound Lines, and Firestone Tire & Rubber Company bought and dismantled Los Angeles Railway's tramway network - a process that went back to history as the Great American Tramway Scandal. A large network of motorways was created in its place. According to the premise of the 1950s, no citizen should live more than six kilometers from a motorway. In 1960, the first office building was built in the former low silhouette of the city, the highest of which until then was the City Hall of 1928.
In August 1965, a major race riot occurred in Los Angeles' southern Watts district. The riots, known as the Watts riots, claimed 32 lives and 874 injured in six days. The damage was $45 million.
The sharp increase in car traffic caused problems from the late 1970s onwards. Smog, decentralization and a sharply rising crime dominated the image of the city. Since the early 1990s, however, LA has been working on the construction of a tramway network, after the millions of city's public transport had to deal with buses for almost three decades. However, the financial and bureaucratic cost of building the metro is much greater than that of building the original network, since not only the city is now much denser but also earthquakes must be taken into account when constructing underground lines.
The riots in Los Angeles from April 29 to May 2, 1992 were one of the greatest racial riots in US history. This was triggered by the acquittal of four white policemen accused of mistreatment of African-American Rodney King. 53 people died in the riots, 2,383 were injured, and the damage amounted to $800 million.
With the end of the Cold War in 1990, an important industry in the city, the aerospace industry, was severely affected. Following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, and the reorientation of the defense strategy to combat terrorism, this industry is once again of great economic and strategic importance to the US. At the beginning of the 21st century the status of the city as a cultural and economic center of the region is undisputed. The problems facing the city are unemployment, huge traffic, environmental pollution, and gang crime.
population
religions
Los Angeles is home to followers of many religions. Among the more than 100 Christian faiths, the Roman Catholic Church is dominant because of the high number of Hispanics. Other important Christian confessions are the Adventists, Baptists, Lutherans, Methodists, Orthodox and Witnesses of Jehovah. Smaller religious groups are followers of the Baha'i religion, Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, Jewish religion, Mormons, Sikhism, Sufism, and Zoroastism.
The Roman Catholic Church of the region is organized in the archdiocese of Los Angeles. It was built on June 1, 1922 as the bistum of Los Angeles-San Diego, and on July 11, 1936 it became the archbishop. With 4.2 million believers (2004), it is considered the largest bistum in the United States. It is one of the typical cardinal seats of the Catholic Church, whose archbishop is available to six bishops to perform his pastoral duties. The parish province today includes the districts of Fresno, Monterey, Orange, San Bernardino and San Diego. Archbishop of Los Angeles has been José Horacio Gómez since 2011. The Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels (Cathedral of Our Lady of the Angels) is the Bishop's Church of the Archbishop of the Archbishop.
In the city, with the "Los Angeles California Temple" built in 1956, the second largest sanctuary (after the Salt Lake Temple) of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormones) stands. The temple is 112 meters long, 82 meters wide and has a height of 78 meters. A statue of the angel and Prophet Moroni is located at the top of the temple tower.
Los Angeles has the third largest Jewish community in the United States (after New York and Miami), with 490,000 people in 2001. Many synagogues are located in the city, most in the San Fernando Valley and West Los Angeles.
Due to the large number of immigrants from Asia, the Buddhist community has seen a strong increase in recent years. Los Angeles currently has the largest Buddhist population in the United States and houses a large number of schools and systems of Buddhism. There are more than 300 Buddhist temples spread across the city.
Since the beginning of the 20th century, many Hindu Swamis and Gurus have practiced in Los Angeles. The Self-Realization Fellowship is based in Hollywood and has a private park in Pacific Palisades. The non-profit religious society was founded in 1920 in Los Angeles by Paramahansa Yogananda as a "Church of All Religion". The founder of the Hare Krishna Movement (ISKCON), Bhaktivedanta Swami, also built here. ISKCON's Krishna Temple in Watseka Avenue is open daily and supported by many Hindus of Indian descent. The Ratha-yatra Wagon Festival at Venice Beach is attended by tens of thousands of people every July.
population
The population explosion in the 20th century - in 1900 the city had only 102,000 inhabitants - hit Los Angeles completely unprepared. New buildings, such as single-family houses, commercial buildings, or shopping centers, were mostly built as flat buildings, which allowed the city to expand enormously. The population continues to grow. Immigration from Latin America, particularly Mexico, as well as from Asia, plays an important role. More than a third of the population of Los Angeles was born outside the US.
In Los Angeles, people from 140 countries live, speaking 224 different languages. According to the 2010 census, the 1.8 million Latinos accounted for 48.5% of the city's total population, which has about 3.8 million inhabitants. 28.7% of the population of Los Angeles belonged to the (non-Hispanic) white population. African-Americans accounted for 9.6% of the population, and the indigenous population was the smallest, with 0.7% and 28,215, respectively. Asians and migrants from the Pacific Islands, mainly Chinese, Japanese, Koreans, Vietnamese, Thais, and Filipinos, are also growing populations. Together with the Iranians, they accounted for 13.0% of the city's total population. 60% of households speak a language other than English, mainly Spanish. However, due to an English-speaking environment, such as school or media, a large proportion of Latinos born in the US speak and understand good English.
Although cultures are very diverse in the city and in Los Angeles County in general, as in all international cities and multi-cultural metropolitan areas, there is a certain division of residential areas by ethnic or cultural origin. Almost always, such "divisions" flow and merge.
Urban areas with a very high proportion of Latinos are, as a rule, East Los Angeles and Montebello, where more and more people from Latin America, especially Mexico, as well as El Salvador and Honduras have settled since the 1970s, and in some cases since the beginning of the century. Moreover, South Los Angeles, also called South Central, is a district with a very large Hispanic population, often exceeding 90% in some eastern districts. Quarters and cities like Huntington Park, South Gate, Lynnwood, Bell (California), Bell Gardens, Lennox, Hawthorne and Westlake are also very Hispanic. Many African-Americans live in the western South of Los Angeles. Likewise, urban areas or cities such as Inglewood, Crenshaw, Leimert Park, Westmont, and Compton are mostly inhabited by black people. Asians, mainly East and Southeast Asians like Chinese, Taiwanese, and Vietnamese of Chinese descent, live mostly in Monterey Park and the Alhambra area in the western San Gabriel Valley. There are also significant populations of Asians in cities in L.A. County such as Torrance, Carson, Gardena, Koreatown and Chinatown. The majority of the white population lives along the Pacific coast from Rancho Palos Verdes to Redondo Beach, Manhattan Beach, El Segundo, Marina del Rey to Santa Monica and between Lakewood and the eastern Long Beach. In addition, a larger white population lives in the area between Santa Monica and Hollywood. The areas in between include West Los Angeles, Culver City, Beverly Hills, West Hollywood and Hancock Park. The neighborhoods on and around the Santa Monica Mountains, such as Pacific Palisades, Brentwood, Westwood, Bel Air, Hollywood Hills, Loz Feliz and Silver Lake, are also mostly white.
According to the 2010 census, there were 3,792,622 inhabitants, 1,413,955 households, and 807,326 families living in the city. The median income per household was $49,497. About 22% of people lived below the poverty line.
On July 1, 2006, 3,877,129 people lived in the administrative city of Los Angeles. The population density was 2,812 inhabitants per square kilometer. The Metropolitan Statistical Area (Metropolitan Statistical Area) was home to 12,950,129 people. The population density was 1,031 inhabitants per square kilometer. The metropolitan area (Combined Statistical Area) was home to 17,775,984 people. The population density was 202 inhabitants per square kilometer.
The following table shows the population of the city according to the area. For the years 1800 to 2010 the census results are given. For July 1, 2013, the United States Census Bureau estimates that the population is 3,884,307. This represents a very high growth compared to the period 1990-2010
|
|
crime
The problem is high crime, especially gang crime. Los Angeles is one of the cities with the highest number of street gangs. The Los Angeles Police Department (LAPD) estimates that more than 400 gangs with at least 39,000 members are active in the city. There are 350 police officers specializing in gang crime.
Some areas are considered very dangerous because of the street gangs, especially at night. This includes many districts in South Los Angeles district, as well as the suburbs of Compton and Lynwood. The murder rate in Compton is about six times higher than the US-wide average.
A total of 132,034 offenses were recorded in Los Angeles in 2006 (142,506 in 2005 and 163,626 in 2004). The overall crime rate fell by 7.3% compared with 2004 and by 19.3% compared with 2005. In 2006, the trend for the individual sectors was as follows (in parentheses, decrease compared to 2005): 481 murders (-1.8%), 903 rapes (-7.2%), 14,235 robberies (+5.5%), 14,118 serious injuries (-9.1%), 20,020 burglary thefts in private homes and buildings (-8.8%) 2%), 29,911 theft from cars (-8.8%), 27,779 theft of personal property/other thefts (-9.3%), and 24,587 theft from cars (-8.1%).
policy
municipal government
The city council of Los Angeles is headed by the Mayor, who is elected by the population for a term of four years. He/she shall appoint heads of the various municipal departments and other officials, in some cases with the approval of the City Council. The mayor has the right to veto regulations.
The City Council of Los Angeles has 15 district council members. It is divided regionally by the districts (districts) of the city. The Assembly of Municipal Representatives adopts laws, sets the property tax and allocates its financial resources to the various municipal departments. City council elections are also held every four years.
Antonio Villaraigosa won the 2005 mayoral elections by a large margin. He took over on 1 January 2006. He is the first Hispanic mayor of Los Angeles since the early 1870s. Cristóbal Aguilar was the last Latino mayor of the city to leave office in 1872.
Villaraigosa began the fight against widespread corruption soon after his inauguration, for example by removing all lobbyists from urban commissions. During his tenure, he discussed the construction of social housing and the construction of public green spaces. He achieved success in public security. The crime rate decreased by 21.8% between 2005 and 2015, with the latest upward trend. In 1992, for example, there were 1094 murders in Los Angeles. For six years (2015 levels), there have been fewer than 300 murders per year, most recently rising from 260 in 2014 to 283 in 2015.
Eric Garcetti has held the post of mayor since the election on May 21, 2013. He is the first Jewish mayor of Los Angeles.
flag
The flag of Los Angeles was designed in 1931 for the 150th anniversary of the city. It consists of three engraved vertical strips in green, gold and red, representing the main fruits grown in California: olives, oranges and grapes. In the middle is the city seal. The seal contains the coat of arms of the city of Los Angeles, consisting of four fields. The four fields include the United States' coat of arms, the flag of California, the coat of arms of Mexico in the version 1867-1968, and the coat of arms of Castile and Leon. The last two represent the history of the city under Mexico. as a Spanish colony. The coat of arms is surrounded by the above mentioned fruits and the legal name of the city (City of Los Angeles) and the date of its foundation (1781).
town twinning
Los Angeles has partnerships with the following cities:
|
|
city friendships
Los Angeles has friendships with the following cities:
- Łódź, Poland (since June 2010)
- London, United Kingdom (since December 2009)
- Manchester, United Kingdom (since December 2009)
Culture and sights
music and theater
On October 23, 2003, Frank Gehry’s Walt Disney Concert Hall opened. The building is home to the Los Angeles Philharmonic Orchestra under the direction of Gustavo Dudamel and the LA Master Chorals. The construction of the concert hall is due to a public-private partnership initiative between Lillian Disney (1899-1997), other members of the Disney family, sponsors and the Los Angeles district. The Los Angeles Opera has its playground at the Dorothy Chandler Pavilion, part of the Los Angeles Music Center.
The Hollywood Bowl, opened in 1922, is located in a hillside area in Hollywood, a natural amphitheater. The Hollywood Bowl Orchestra is located here, and during the summer season the Los Angeles Philharmonic Orchestra is also located there. The Beatles, Frank Sinatra and Mikhail Baryshnikov are just some of the legendary artists that have appeared here. A number of concerts take place there during the summer months and access to the grounds is free of charge every day throughout the year.
The Theater District on Broadway is home to numerous large theaters. Built in 1893, the Bradbury Building with its sun-drenched atrium, stylish wrought-iron balconies was seen in the film Blade Runner, just like the neighboring cinema million dollars theater from 1918, which now houses a communal hall that is widely accessible shelter. The first movie in the United States, the Electric Theater, opened in Los Angeles in 1902.
The more extravagant Los Angeles Theater was completed in just 90 days for the premiere of Charlie Chaplin's film lights in the city and invites Cineasten to its screening room every June during the film festival Last Remaining Seats. The Orpheum, a magnificent example of the Neo-Renaissance, with its large staircases and magnificent chandeliers, is one of the traditional casinos regularly used.
The Grauman’s Chinese Theater stands on Hollywood Boulevard. It opened in 1927 in the style of a Chinese pagoda. The cinema became world famous thanks to the hands and shoemakers of numerous movie stars, who were perpetuated in cement blocks in the entrance to the cinema. The Grauman’s Egyptian Theater, opened in 1922 in a pseudo-Egyptian style, and the Dolby Theater (until February 2012 Kodak Theater), where the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (Academy Awards) have been awarded since 2002 will be awarded.
museums
Los Angeles and the Greater Los Angeles are home to hundreds of museums and collections with different focal points.
The largest and oldest art museum in Los Angeles is the Los Angeles County Museum of Art on Wilshire Boulevard, founded in 1910. It houses a collection of over 100,000 works from antiquity to the present. This makes it the largest museum in the United States west of Chicago. The collections of American, Islamic and Korean art are particularly extensive and significant.
Another important art museum is the J. Paul Getty Museum. It was founded in 1953 by the oil billionaire J. Paul Getty was originally founded in a replica of the Villa dei Papiri of Herculaneum in Malibu (Getty Villa). Since 1997, it has been located at the Getty Center in Brentwood, a district of West Los Angeles in the Santa Monica Mountains, along with other scientific institutions, such as the Getty Research Institute, the Getty Conservation Institute, which is active in restoration and the Getty Leadership Institute, which is dedicated to the education and training of museum leaders caring. The complex was designed by the architect Richard Meier, who was commissioned to design the building in the mid-1980s. Construction began in 1991 and continued until 1997. The free museum collects antiques, drawings, book paintings, paintings, photography as well as sculpture and handicrafts.
The California Plaza, on Grand Avenue, is home to the Museum of Contemporary Art, opened in 1986. The complex is a playful arrangement of red geometric blocks designed by the architect Isozaki Arata, who called him "a small village in the valley of skyscrapers." It houses an impressive collection of paintings and sculptures by Franz Kline, Mark Rothko, Robert Rauschenberg, Claes Oldenburg and Antoni Tàpies.
The Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, located in the Exposition Park and founded in 1913, is the third largest natural history museum in the United States. It has important collections of fauna and flora, including dinosaurs, as well as the history of the city. Nearby is the California Science Center. Natural museums include the George C. Page Museum at La Brea Tar Pits on Wilshire Boulevard.
Among the many museums in the greater Los Angeles area are the Hammer Museum (with a collection of mostly old masters and French impressionists), the Southwest Museum (it houses mainly Indian exhibits), the Los Angeles Museum of the Holocaust, the Museum of Jurassic Technology and the Huntington Library (with a collection of manuscripts, books and paintings in particular) . Santa Monica is home to the Santa Monica Museum of Art on Michigan Avenue, with a collection of contemporary art. The General Phineas Banning Residence Museum in Wilmington, housed in a Greek Revival-style building, houses a collection of 19th century postcards and an exhibition about the history of the Port of Wilmington.
structures
The Civic Center houses several government buildings (including the City Hall, Los Angeles City Hall) and the Los Angeles Music Center with the concert hall Dorothy Chandler Pavilion, the Ahmanson Theater, the Mark Taper Forum and the Walt Disney Concert Hall.
In September 2002 the Catholic Cathedral Our Lady of the Angels was inaugurated in the center of the city; the church building, designed as a postmodern interpretation of a Spanish mission station, with a 40-meter-high bell tower, is part of a cultural area designed to revive the city center. The Farmers Market, Chinatown, Little Tokyo and the nearby Culver City are also interesting. The Great Western Forum is located in the suburb of Inglewood.
The Universal Studios in Universal City, the Warner Bros, are well worth a visit. studios in Burbank and CBS Television City in Hollywood. The Hollywood Sign (Hollywood sign) is located in the north of the city and can be seen from the Griffith Observatory. The Hollywood Boulevard in the city center is home to theaters and cinemas (Grauman's Chinese Theater, Grauman's Egyptian Theater, Kodak Theater and others), as well as the famous Hollywood Walk of Fame, where numerous stars were invited to honor celebrities.
Other attractions include the 335-meter high Wilshire Grand Tower (the twentieth highest building in the United States and the tallest west of the Mississippi), the U.S. Bank Tower, the Aon Center, the Bank of America Plaza, the City National Tower (formerly Bank of America Tower), and the Staples Center (all in downtown).
Alameda Street in Downtown is home to the Los Angeles Union Station, which was completed in 1939, Los Angeles Central Station. The architecture combines Spanish colonial style, Mission Revival and late Art Deco with Moorish architectural elements. The Los Angeles Public Library on Fifth Street is a rather hidden architectural gem. The library includes old painted wooden ceilings and a church-like tower hall.
The 13-story Eastern Columbia Building is located in the Broadway Theater District. The Art Deco building was opened in 1930 by architect Claud Beelman. The distinctive Watts Towers are located in the Watts district and the Capitol Records Building in Hollywood. The Magic Castle is the private club house of the Academy of Magical Arts, a magician club located on Franklin Avenue in Hollywood.
From the Getty Center, Dodger Stadium in Elysian Park or Mount Wilson, there are wide views over the city area in good weather. The Encounter Restaurant at Los Angeles International Airport is considered by Angelenos to be the secret landmark of the city.
The best-known hotels in Los Angeles are the Beverly Wilshire (built in 1928), the Chateau Marmont Hotel in West Hollywood (built in 1929 following the example of Chateau Amboise in the French Loire Valley), the Beverly Hilton Hotel (1955 Mondrian Hotel (1959) in West Hollywood and Westin Bonaventure Hotel (1976) in Downtown.
Los Angeles and its surroundings are home to many masterpieces of villas. These include the Gamble House of Architects Charles and Henry Green, Richard Neutras Lovell House and the buildings of Irving Gills. Many of the buildings of the architect Irving Gill, who is almost unknown in Europe, have been destroyed or extensively altered, resulting in the progressive loss of his work.
Other examples of residential architecture include the Schindler House of the architect Rudolph Michael Schindler in West Hollywood, Frank Lloyd Wrights Hollyhock House in Little Armenia and Ennis House in Los Feliz. The Hollyhock House in particular is one of the most important works of Wright. The house is reminiscent of a Mayan temple from Central America with its smooth plaster and pre-concrete ornaments. In the courtyard there are water games in the shape of an amphitheater.
Other remarkable buildings are by John Lautner, a disciple Frank Lloyd Wrights. The most famous example is the Malin Residence that was created in 1960, also called the Chemosphere. Built on a steep embankment above the San Fernando Valley, the building resembles an eight-edged UFO, with a single concrete pillar bearing the construction, which actually enhances the effect of floating.
There are also the so-called concept houses scattered throughout the city, including Pierre Königs Bailey House, also known as Case Study House No. 21 and the Stahl House (Case Study House No. 22). Both houses were built on land previously considered unbuildable. They can be visited as well as the Eames House of designer Charles Eames and his wife, the artist Ray Eames in Santa Monica.
park
The parks in and around Los Angeles contain numerous leisure and cultural facilities.
In El Pueblo de Los Angeles State Historic Park is the Plaza Church, completed in 1822. The Griffith Park, by far the largest park in Los Angeles, houses the Gene Autry Western Heritage Museum, an observatory, a planetarium, and Los Angeles Zoo. The Exposition Park is home to the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, a museum of science and industry and a natural history museum.
In the central Elysian Park is the Dodger Stadium (Chavez Ravine) and the L.A. Police Academy. The Echo Park is also right in the center of Los Angeles. Echo Park Lake served as a backdrop in the successful movie Chinatown.
Not only for children are the theme parks Disneyland and Disney’s California Adventure with the 30 meter high Grizzly Peak in the nearby Anaheim. Near the city there are the Angeles National Forest and the endless Pacific beaches - the Los Angeles coast stretches for about 115 kilometers - in Santa Monica or Venice Beach.
The Hancock Park of Los Angeles houses the La Brea Tar Pits, a collection of pits of various sizes filled with natural asphalt. Rancho La Brea's high asphaltic sediments are known as one of the most fossil-rich sites of the Pleistocene or Ice Age. The George C. Page Museum houses an exhibition of animal skeletons, including an extensive collection of skulls of the Canis, an extinct wolf-like dog. Also in Hancock Park is the Los Angeles County Museum of Art with its art collection.
The Universal Studios Hollywood is a theme park divided into two sections: the Upper Lot and the Lower Lot. Both are connected by the world’s largest and highest escalator construction, which extends over several levels. The Upper Lot extends from the entrance of the park to the The Simpsons Ride, where the escalators lead to the lower part of the park. In addition to extensive live shows, the Upper Lot also offers the actual Studio Tram Tour, which is a main attraction. The Lower Lot is located in the heart of the studios and offers three attractions, the Jurassic Park - The Ride, Transformers the Ride 3D and Revenge of the Mummy.
sport

The most popular sports in Los Angeles include, in particular, the team sports American football, baseball, basketball and ice hockey. Soccer, lacrosse and volleyball are also very common. Individual sports such as bowling, golf, athletics, swimming and tennis are also very popular.
football
Los Angeles hosted the 1932 Summer Olympics and the 1984 Summer Games and will host the Games for the third time in 2028. Among the many sporting events in the city are the annual Los Angeles Marathon and the ATP Tour's Country Wide Classic Tennis Tournament. Many well-known sports clubs are located in Los Angeles and its surroundings.
In college football, two successful teams are based in Los Angeles with UCLA Bruins and USC Trojans. Both teams play at the Pacific-12 Conference of the National Collegiate Athletic Association.
In 1926, Los Angeles Buccaneers established a team for the National Football League in the city. However, this team could not play home games and played only one season. Rams, originally based in Cleveland, played in Los Angeles in the 1946 NFL season. At the same time, the Los Angeles Don also hosted the competing All-America Football Conference. After the defeat of the AAFC at the end of the 1949 season, the Rams remained the only professional football team in the city. It was played in the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum. In 1960, the newly established American Football League team was established in the city. However, this team moved to San Diego in the following season.
In 1984, the Oakland Raiders moved to Los Angeles after the team owner failed to agree on a new stadium construction with the city of Oakland. The Raiders also played in the Memorial Coliseum. In 1995, the Rams moved to St. Louis and the Raiders moved back to Oakland, as the city of Los Angeles was not able to agree on the construction of a new stadium at the beginning of the 1990s.
The new owner of the Rams, E. Stanley Kroenke, managed to build a new stadium in Los Angeles. This was the basis for the team's return to Los Angeles in 2016, before moving to Las Vegas in 2020. With the start of the 2017 season, the Chargers moved back to Los Angeles, which since the 2020 season have been playing at the newly built SoFi Stadium.
ice hockey
The Anaheim Ducks is an ice hockey club that plays in the National Hockey League (NHL). In the 2006/07 season they won the Stanley Cup and the division title for the first time. The Conferences also won the 2002/03 and 2006/07 season. Founded in 1992, the club is hosting its home games at the Honda Center, which has 18,000 spectators.
Los Angeles Kings is an ice hockey team that plays in the National Hockey League (NHL). The biggest successes were the double win of the Stanley Cup, the team celebrated smaller successes in the early 1990s. The team was founded in 1967 and carries its home games at the Staples Center (capacity: 18,000 viewers). From 1988 to 1996, Wayne Gretzky, one of the most successful ice hockey players in the world, played at the kings.
baseball
Los Angeles Angels of Anaheim is a baseball team that plays in the Major League Baseball (MLB). The biggest success was the World Series 2002 title. The club, which was founded in 1961, carries its home games at the Angel Stadium of Anaheim (capacity: 45,000 viewers).
Los Angeles Dodgers is a baseball team that plays in the Major League Baseball (MLB). The L.A. Dodgers were born from the Brooklyn Dodgers in 1959. So far, six World Series titles have been won. The team will perform its home games at the 56,000-spectator Dodger Stadium.
basketball
The Los Angeles Lakers are a team of the National Basketball Association (NBA). The team won a total of 16 championships - the second most behind the Boston Celtics - as well as 28 Conferent titles and 26 Divisional titles. Since the league's founding days, the Lakers have belonged to the NBA, as well as to the most successful teams. The home theater is the Staples Center.
Los Angeles Clippers is a second team at the National Basketball Association (NBA).
Los Angeles Sparks play in the Women’s National Basketball Association (WNBA).
soccer
LA Galaxy is a football team that plays in the Major League Soccer (MLS). The biggest successes were the winners of the CONCACAF Champions Cup 2000 and the national championships 2002 and 2005. Founded in 1995, the team plays home games in the Home Depot Center (capacity: 27,000 viewers). The most prominent football player is David Beckham, who played his first game for Galaxy on July 21, 2007 and was on contract until January 30, 2013.
motorsport
In August 1982, the Speedway Single World Championship Finale in 1982 was held in Los Angeles Coliseum in front of more than 30,000 spectators, and the American Bruce Penhall won, defending his World Cup title, before he announced his resignation after the race and went to Hollywood as an actor.
leisure and relaxation
One of the most popular beaches on the Pacific coast of Los Angeles is Venice Beach. At the Venice Boardwalk, the wide promenade, also known as the Ocean Front Walk, numerous musicians, painters and artists meet at weekends (in summer daily). At night, Venice Beach is a dangerous place because of the street gangs and dealers. It is forbidden to stay on the beach after sunset.
Located on palm-lined beaches and hills overlooking the Pacific, just north of Venice, Santa Monica is the oldest, largest and most famous seaside resort in the metropolis. This liberal, health-conscious district is home to many writers and rock stars. The place is also known for its strict rent price controls and construction regulations.
The Malibu beach colony is also well known and is inhabited by many celebrities. Surfrider Beach, south of the pier, has been a popular surfing spot since the 1950s. A large part of the "Malibu Creek State Park" on Las Virgenes Road further north, not far from Mulholland Drive, belonged to the studios of the 20th Century Fox. Many Tarzan movies were shot on the slopes covered by evergreen bushes. There is a lake, several waterfalls and hiking trails in the 10,000-acre park.
Along the coast to the south of Los Angeles, the Pacific Coast Highway passes the runways of the LAX airport and leads to a coastal strip with several beaches of South Bay: Manhattan Beach, Hermosa Beach and Redondo Beach. Long Beach has invested a lot in recent years, creating a number of new office buildings and hotels. The biggest attraction of Long Beach is the steamer Queen Mary, from the 1930s to the 1960s the flagship of the Cunard Line, it is now a hotel.
Regular events
spring
Every year on Easter Sunday, the Easter Sunrise Service at the Bowl takes place, an Ecumenical Easter service in the early morning at the Hollywood Bowl in Hollywood. The Jimmy Stewart Relay Marathon, a charity relay race, will take place in the middle of April in Griffith Park. Other events in the month of April include the Rosenblossom Festival at Exhibition Park Rose Garden, the L.A. Times Book Festival at the campus of the University of California, Los Angeles, the Pacific Islander Festival at the Ken Malloy Harbor Regional Park, the Fiesta Broadway at the Homestead Museum and the Springfest. on campus at the University of Southern California.
At the beginning of May, the Native Americans will meet for the UCLA Pow Wow at the Intramural Field, UCLA Campus. You can see traditional music, dance and handicrafts. Celebrations in May are the Cinco de Mayo, a street festival in downtown and the Family Fun Festival, a Japanese cultural festival celebrating the Children's Day in Little Tokyo.
Also in May, the Valley Greek Festival will be held in St. Sophia Cathedral, the NoHo Theater & Arts Festival on Lankershim Boulevard and Magnolia Avenue in North Hollywood and the UCLA Jazz Reggae Festival at the Intramural Field, UCLA Campus. Last Monday in May, the Memorial Day Parade will take place in the Canoga Park, San Fernando Valley.
summer
Many festivals are organized in June. These include the Playboy Jazz Festival and the Mariachi USA Festival at the Hollywood Bowl. Other festivals include the Los Angeles Independent Film Festival (Directors Guild of America, Sunset Boulevard) and the Hollywood Ha-Ha Comedy Festival (Noho Arts District, North Hollywood). The Hollywood Bowl Summer Festival takes place in the Hollywood Bowl from late June to mid-September.
The Independence Day celebrations will be celebrated throughout the city on July 4. Also in July there is the Outfest - LA Gay and Lesbian Film Festival (gay and lesbian film festival), Echo Park Lake the Lotus Festival and Los Angeles Tennis Center in Westwood the men's tennis tournament countrywide Classic of the ATP Tour. There are also numerous festivals in August. These include the Nisei Week Japanese Festival, a Japanese culture festival in Little Tokyo, the Los Angeles Festival in many places in the city, and the JVC Jazz Festival in the Hollywood Bowl.
The Sweet & Hot Jazz Festival takes place from August to September at Los Angeles Airport Marriott Hotel. El Diecisis de Septiembre, the celebrations for Mexican Independence Day, will be on September 16 in Broadway and South Los Angeles. Events in early and mid-September are the Port of Los Angeles Lobster Festival, a Hummerfest at the Harbor Waterfront and the Autumn Moon Festival in Chinatown.
autumn and winter
In October, the Hollywood Film Festival takes place in various locations in Hollywood and the Los Angeles International Short Film Festival at Los Angeles Film School in Hollywood. November is the AFI Los Angeles International Film Festival in various places in the city, the Mariachi Festival (Mexican Music Festival) at the Mariachi Plaza in Boyle Heights and the Hollywood Christmas Parade on Sunset Boulevard in Hollywood.
From the end of November to the end of December, the Griffith Park Light Festival in Griffith Park, Downtown is on display. The Martin Luther King Kingdom Day Parade, a parade commemorating Martin Luther King's birthday on January 15, moves from Martin Luther King Boulevard to Western Boulevard on Martin Luther King Day.
February is the Pan African Film & Art Festival, hosted by Magic Johnson Theater at Baldwin Hills Crenshaw Plaza and the New Year's Chinese Festival with Golden Dragon Parade in North Broadway, Chinatown. Also in February, the Oscar ceremony will take place at the Kodak Theater in Hollywood. The Los Angeles Marathon will be held in early March. It runs from Grand Avenue through the entire center of Los Angeles.
gastronomy
Los Angeles offers a wide range of international restaurants and restaurants. Among the popular dishes are traditional American cuisine with lots of meat and potatoes, Korean tempura dishes, sushi, Japanese dishes with urdon and soda, Mexican enchilades and tamales, spicy burritos and pastrami sandwiches.
There are also Chinese restaurants where you can enjoy abalons, crabs, shrimps and ducks. You can also enjoy a sandwich with turkey, pork, beef or lamb, as well as Italian Ossobuco and risotto. The Cajun cuisine, also available in Los Angeles, offers Cajun Country specialties.
trade
One of the most famous shopping streets is Rodeo Drive in Beverly Hills, a suburb of Los Angeles. Numerous well-known fashion brands can be found here. The street also houses the most expensive shopping centers in the world. They include The Rodeo Collection with five levels of sales above and below the ground, and Two Rodeo, which gives the impression of two small European cobblestone streets with fountains, piazza and balconies. At the end of the street are other large department stores, including Barneys New York and Saks Fifth Avenue.
Shops of department stores Macy’s and Bloomingdale’s are located in the nearby Beverly Center and Westfield Century City (formerly Century City Shopping Center & Marketplace). The shopping center in Century City, an example of the modernism of the 1960s, was built without a roof in the style of a market square.
The Melrose Avenue, located between Santa Monica Boulevard and Hoover Street in Silver Lake, is home to a large number of retail outlets. The best known is the Red Balls boutique, which can be seen in the advance of the TV series Melrose Place. Another shopping promenade is Universal CityWalk next to Universal Studios Hollywood. There are numerous shops and restaurants. There are also many department stores and galleries in downtown Los Angeles, including the Grand Central Market on South Broadway. On offer are freshly prepared specialties, fruits and vegetables.
Economy and infrastructure
economy
The city is a leading production, commercial, transport and financial center in the USA. It is home to the chemical industry, electronics, clothing and food industries, metal processing, construction and publishing. Los Angeles is the world's largest location for the aerospace industry and an important center for cinema, radio, television and music production. Tourism also plays an important role in the economy of Los Angeles. With 5.6 million foreign visitors, Los Angeles was 21st in the world's most visited cities in 2016. Tourists in the city spent $8.1 billion in the same year. Most foreign visitors came from Asia, Europe and Latin America.
In 2010, the city's unemployment rate was, on average, 13.9% higher than that of the state of California (12.4%) and higher than the national average in the US (9.6%). The trend in recent years has been as follows: 2006 (5.3%), 2007 (5.6%), 2008 (8.3%), 2009 (12.7%) and 2010 (13.9%).
By the late 1990's, Los Angeles was home to many major financial institutions in the West of the United States. Mergers with other institutes led to the transfer of headquarters to other cities. For example, in 1992, Security Pacific Bank merged with Bank of America, in 1996, First Interstate Bancorp merged with Wells Fargo, and in 1998, the Great Western Bank merged with Washington Mutual. Los Angeles was also the seat of the Pacific Exchange until it closed in 2001. In a ranking of the world's most important financial centers, Los Angeles ranked 17th (status: 2018).
Numerous large companies and companies as well as research institutions have their headquarters in the city. These include entertainment companies such as 20th Century Fox, DreamWorks SKG, Paramount Pictures, The Walt Disney Company and Warner Bros., the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (known by the Oscar Award), toy manufacturer Mattel, computer game makers Activision and THQ, Northroe aerospace group p Grumman, the space consortium Sea Launch, the oil and gas supplier Unocal, the RAND Corporation (think tank for the US Armed Forces), ICANN (manager of names and addresses on the Internet), the Hilton hotel chain, the construction group KB Home and the publishing company Tokyopop.
The three Fortune 500 companies AECOM, CBRE Group and Reliance Steel & Aluminum Co. also have their headquarters in Los Angeles.
Many laboratories and research centers belonging to the NASA space organization, such as the Dryden Flight Research Center, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex, are located in the Los Angeles metropolitan area.
In 2018, Los Angeles ranked 64th out of 231 cities worldwide surveyed in a ranking of cities for their quality of life.
traffic
long distance
motorway
Los Angeles is connected to all major cities in the country via a well-developed network of interstate and interstate highways.
At Interstate 5, you can reach from Los Angeles the northern city of Seattle in Washington State and in the southern direction of San Diego, the second largest city in California. The Pacific Coast Highway (State Highway 1) runs north along the California coast to Santa Barbara and San Francisco. Interstate 10 connects Los Angeles with Phoenix (Arizona), Interstate 15 with Las Vegas (Nevada) and Salt Lake City (Utah), and Interstate 40 with Oklahoma City (Oklahoma) and Memphis (Tennessee).
In particular, the overland bus service, such as Greyhound Lines, is of great importance for traffic within the state of California, and in some cases also for long hauls.
rail
The city is an important railway junction (transcontinental and regional). The Amtrak railway company operates trains from Los Angeles via Van Nuys to Bakersfield. In Los Angeles, there is a transfer to the Pacific Surfliner, which runs from San Diego via Los Angeles to San Luis Obispo. The Union Station in Los Angeles is the terminal for many major routes that pass through the southern part of the Rocky Mountains. It is also the farthest train station in the south along the west coast to Seattle. The regional metrolink rail network in southern California connects Los Angeles to all major cities in the region. From Union Station you can take the underground (red line) to Downtown, Hollywood and other places.
air
The Greater Los Angeles has many airports. The largest is Los Angeles International Airport, also known by its IATA acronym LAX, located southwest of the city center. It has four runways and ten handling halls. It handles more than 80 million passengers per year. With this traffic, the airport has been among the top 10 of the world’s largest airports for many years.
The airports
- Long Beach Airport (Daugherty Field, Long Beach)
- John Wayne Airport (Orange County)
- Hollywood Burbank Airport (Burbank)
- Ontario International Airport (Ontario)
mainly serve national objectives and are significantly smaller;
- Santa Monica Municipal Airport (Santa Monica)
- Zamperini Field (Torrance)
- Van Nuys airport (Van Nuys)
operate private air services.
shipping

The port of Los Angeles in San Pedro bay is North America's largest container port and the world's tenth largest. In 2006, the volume of containers was 8.5 million TEU (20 ft containers), compared to 7.5 million TEU in 2005. The port, which was created by the creation of a Board of Harbor Commissioners on 9 December 1907, occupies an area of 30 square kilometers on a 69-kilometer coastline. Adjacent is the separate port of Long Beach.
The port of Los Angeles is the largest center for passenger shipping on the west coast of the United States; from here, over a million passengers are transported annually. The renovated World Cruise Center is known as the safest passenger shipping complex in the United States. The port is served by the Pacific Harbor Line (PHL). From there, the intermodal railway wagons pass through the Alameda Corridor to Los Angeles.
local traffic
Los Angeles does not have a traditional transport network, as it is known from Germany and other countries. In general, the metro, buses and regional trains (metrolink) operate as separate transport companies and new tickets must be purchased at the change-over. In addition, the bus has to be paid appropriately, the bus drivers do not have any change. This has changed with the introduction of the Transit Access Pass (TAP) in 2007, similar to the Oyster Card in London. With the exception of the Metrolink train, for which an extra ticket must continue to be purchased, the TAP card can be used and paid for all metro trains, express buses and ordinary buses, but also many buses in Los Angeles County, the LAX Airport's FlyAway, and even the Metro Bike Share (Metro Bike Share) accept the card. From November 29, 2019, only the TAP card can be used as a means of payment at the Metro ticket machines.
rail
On July 3rd, 1873 the first horse trams went in the city. In 1885, the tram system was electrified. It became famous under the name of "Red Cars", although only the long-distance connections to San Fernando Valley and Orange County were painted red, the wagons in the limits of the city of Los Angeles were yellow/white. In 1925, the Red Car network experienced the largest expansion with approximately 1,900 net kilometers and the highest number of passengers during World War II. But, as early as 1936, automobile companies such as General Motors started to buy and gradually close privately owned tramways through forward-looking companies and to replace them with bus lines from their vehicle manufacturers (the so-called Great American Tramway Scandal). On March 31, 1963, the network ceased to operate in favor of private transport, and the last train from downtown to Hollywood was labeled "into oblivion," meaning "to forget." Many Freeways were built on the tracks of the Red Cars. However, many track systems are still maintained and equipped with the right-of-way, which would make reactivation easier. After 27 years of interruption, a tram in Los Angeles was again running on July 14, 1990. Today, the 117 kilometers of tram network is part of the Los Angeles metro.
The Metro network has six lines, but only the Red Line and the Purple Line are full subways, the other four are light rail. The Red Line opened its operations on a 28-kilometer stretch on 30 January 1993. The system, also known as MetroRail, is operated by the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (LACMTA). Since the 1980's, the city has invested several billion dollars in the renewal of the rail network - with only modest success. At present, the urban area is so far apart that it is difficult to reach any stops on foot. Work on a metro network was temporarily suspended as the costs on the West Coast, which was at risk of earthquakes, were too high. However, the city rail network, which is mainly on the surface, is being expanded more quickly. After the Blue Line (1990), the Green Line (1995) and the Gold Line (2003), the Expo Line opened the fourth tramway in Los Angeles in 2012. It connects the city center to the Pacific coast at Santa Monica. Between 2006 and April 2012, the first nine miles (14.5 kilometers) long section between stops 23. street and Culver City, the extension to the Pacific coast was opened in May 2016.
Two bus lines, the Orange Line and the Silver Line, are referred to as metrobus and also mentioned on the metro route map. These are express buses, which usually run on their own roads and rarely stop.
Bicycles are available free of charge in the metro trains as well as in the metro buses. All buses have a wheeled beam for two to three wheels on the front. The metro trains have special parking areas for wheels marked with a yellow wheel symbol. In contrast to the metrolink trains, you can also take e-bikes with you at the metro.
Metrolink is a seven-line rail suburban transport service in the greater area of Los Angeles, California. All lines start at Union Station of Los Angeles. Metrolink trains are mainly adapted to suburban commuters in the morning and evening from Los Angeles, so at weekends connections are reduced to about a third of those on weekdays. The maximum speed of the trains is relatively high at up to 140 km/h for American conditions. Almost all double-deck wagons are used.
Bicycles are available free of charge on all metrolink trains. Each wagon can hold up to three wheels. Some trains also have a yellow bike car trolley where up to nine bikes can be transported.
Metrolink tickets are also valid for the metro and buses of Los Angeles.
road
Trolleybuses operated between 11 September 1910 and 1915, between 1922 and 1937 and between 3 August 1947 and 31 March 1963. Buses run every 15 minutes between 5 a.m. and 2 a.m. along the main roads, and there are also express and night lines. There are many bus terminals where schedules are available.
The city's bus network is the backbone of public transport, but it is mostly used by less earners. The metropolitan area is served by numerous bus companies, the largest of which is the public "Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority" (LACMTA), which operates a network of approximately 8,000 kilometers long with 2,600 buses. The Santa Monica Big Blue Bus Line and Orange County Transit buses operate in the north and north-west parts of the country. In the airport area, the Culver City Bus Company serves a small network of routes.
The LACMTA buses, which also operate the metro, consist of three categories. The orange local buses run most of the main roads and stop at a short distance (200 meters). You have line numbers from 1-399 and 600 numbers. The metro-rapid buses are red and usually run the same lines as the local local buses, but they stop only at the major junctions. The line numbers are 700s and 900s numbers. In addition, there are eight express bus lines, the Metro Express buses, which are mainly operated by motorways and very rarely operate. The color of the Metro Express buses is mainly orange, older buses also wear a dark blue paint. Line numbers have numbers around 500.
In total, only about 10% of the city's inhabitants use public transport. Nine out of ten employees drive their own car to work. Los Angeles has the highest density of cars in the world. Multi-lane highways in the United States have become a symbol of 20th century traffic. Despite the well developed motorway network, Los Angeles is usually not a very fast road. The individual motion by car and the air pollution (smog) generated by it are problems of first rank today.
In Los Angeles, millions of professional commuters travel on highways for about an hour on average. The result is immense congestion caused by the extensive settlement structure. In the 1920s, California's metropolis still owned the world's largest urban rail network. Even then, they were not as compact as they were in Europe. In the following decades, the tramway was gradually replaced by the car. To reduce congestion, motorways have been extended to up to 15 lanes since the 1940s. In addition, the creation of the so-called Diamond Lanes, which are reserved for driving communities, is trying to promote the formation of driving partnerships and thus reduce traffic.
media
The largest daily newspaper in the region is the Los Angeles Times, La Opinión is the largest Spanish-language newspaper. Investor’s Business Daily has its offices in Los Angeles, with headquarters in Playa Del Rey.
There are also a number of smaller regional newspapers, alternative weekly newspapers, and magazines, including the newspaper Daily News (with a focus on San Fernando Valley), LA Weekly, Los Angeles CityBeat, LA Record, Los Angeles Magazine, Los Angeles Business Journal. aily Journal", The Hollywood Reporter and Variety, and Los Angeles Downtown News.
In addition to the English and Spanish-language newspapers, numerous local journals for immigrants are published in their native languages, including Armenian, Korean, Dutch, Persian, Russian, Chinese and Japanese. Many cities around Los Angeles own their own daily newspapers, some of which are also read in Los Angeles. Examples are "The Daily Breeze" (for the South Bay), and "The Long Beach Press-Telegram".
Broadcasting
The Greater Los Angeles has a wide variety of local radio and television stations and is the second largest media market in North America (after New York). The first radio station in Los Angeles was KNX. It began broadcasting experimental programs in 1920 and obtained a commercial broadcasting license in December 1921. The first television station in Los Angeles (and the first in California) was KTLA, which began broadcasting programs on January 22, 1947.
The large TV stations in Los Angeles connected to a network are KABC-TV 7 (ABC), KCBS 2 (CBS), KNBC 4 (NBC), KTTV 11 (FOX), KTLA 5 (The CW), KCOP-TV 13 (MyNetworkTV) and KPXN 30 (ION Television). There are also three PBS stations in the region, including KCET 28, KOCE-TV 50, 58 and KLCS. World TV operates stations KNET-LP 25 and LP KSFV-6 on two TV channels. There are also several Spanish-language TV networks, including KMEX-TV 34 (Univision), KFTR 46 (TeleFutura), KVEA 52 (Telemundo) and KAZA 54 (Azteca América). KTBN 40 (Trinity Broadcasting Network) is a religious station.
Several independent TV stations are located in the region, including KCAL-TV-9 (owned by CBS Corporation), KSCI 18 (mainly focused on programs in Asian languages), KWHY-TV 22 (broadcast in Spanish), KNLA-LP 27 (Spanish), KSMV-LP 33 (Variety), KPAL-LP 38, KXV LA 44, KDOC-TV 56 (focusing on classic programs and local sports clubs), KJLA 57 (Variety), and KRCA 62 (Spanish).
film industry
Hollywood is not just a part of Los Angeles, but a synonym for the US film industry. Founded on 1 February 1887 by the Wilcox family, the village was once the site of one of the largest Presbyterian churches in the country and was still around 13 kilometers from Los Angeles in 1900. He began his career in 1911 when David Horsley’s Nestor Company opened the first studio here. It is now a museum and houses a collection of interesting silent-film memorials.
In 1911, 15 other "independents" relocated companies from New York, then the center of the film industry. There were several reasons for this move. The most important were the more suitable climate and the longer days (at that time there was no adequate artificial light, so you would either shoot outdoors or in a studio with a glass roof or similar). The distance from New York, from where the powerful Motion Picture Patents Company (MPPC) threatened all unaffiliated companies with high fines and royalties, was undoubtedly also crucial.
The new industry expanded rapidly and brought rapid success and wealth. Numerous directors and producers, such as Cecil B. DeMille, Samuel Goldwyn, Jesse L. Lasky and Adolph Zukor had opened offices in Hollywood. But only with D. W. Griffith’s silent film The birth of a nation (1915) developed the film production into an independent industry with appropriate technology and specialization. Many smaller companies went bankrupt at that time or were taken over by the large studios, which in the 1930s moved almost invariably to new locations outside Culver City, Burbank, or West Los Angeles. Of the great names, only Paramount Pictures remained in Hollywood. In 1927, Los Angeles had 247 film companies, 58 large film makers, and about 800 long films.
The decline of studios in the 1950's was attributable not only to the US government's anti-trust legislation, but also to the recovering film industry abroad after World War II, and, of course, to television. A new upswing began only in the 1970s and 1980s by directors such as Steven Spielberg and George Lucas. They developed the concept of blockbuster - a high-priced, multi-effects monumental film that was intended to reach as wide a audience as possible. Thanks to a trend that began then and the financial consolidation of US media companies, Hollywood is still a symbol of the lasting success of the US film industry and professionally produced, entertaining films with world-famous actors and happy endings.
Its proximity to the film industry made the city itself the scene of many films.
education
The city is home to many important universities, universities, research and educational institutions.
California State University, Los Angeles (CSULA) is one of three state universities in Los Angeles. It has 21,000 students enrolled in it. The CSULA was founded in 1947 as Los Angeles State College and renamed California State College at Los Angeles in 1964. In 1972, she became a member of the California State University system.
Another state university is California State University, Northridge (CSUN). She is one of the largest universities in the California State University system. The college was opened in 1958 as San Fernando Valley State College and was named in 1972. It has about 33,000 students enrolled in it.
The State University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) was founded in 1919 and is the second oldest campus of the University of California. In 2003, some 37,000 students were enrolled. The 12 faculties employ more than 22,000 people. The Anderson School of Management - one of the best-known business schools in the United States - is part of UCLA.
The University of Southern California (USC) is the oldest private university in Southern California. It opened in 1880. In the early days, a new faculty was added almost every year. Today, it employs some 3,000 full-time teachers, and about 32,000 students are enrolled.
Loyola Marymount University (LMU) is one of the 28 member universities of the Association of Jesuit Colleges and Universities. About 9,000 students are currently enrolled. The university was founded in 1973 by the association of Marymount College with Loyola University. The origins of the educational establishment date back to St. Vincent’s College, which opened in 1865.
Los Angeles public schools are managed by the United School District of Los Angeles (Los Angeles Unified School District). Crenshaw High School is well known in the South Los Angeles district, where about 2,600 students are currently studying. Among other things, the high school was the location of the films Boyz n the Hood - guys in the 1991 quarter and Love & Basketball from 2000. The TV series Moesha (1996-2001) also plays at school.
In 1986, Los Angeles Public Library, Los Angeles's central public library (2.1 million volumes), had two major fires. The establishment was completed in 1926 and reopened in 1993 after a reconstruction. Since 2001 the library has been named after the former mayor of Los Angeles, Richard Riordan.
Sons and daughters of the city
The city is home to many prominent figures. These include the actors Bridget Fonda, Jodie Foster, Angelina Jolie, Elizabeth Mitchell, Marilyn Monroe, Mary-Kate and Ashley Olsen, Gwyneth Paltrow and Anna May Wong, the actor Leonardo DiCaprio, the actor and singer David Faustino, the producer and rapper Dr. Dre, the Rapper apper and actor Ice Cube, rapper The Game, singer and producer Michael Landau, singer and pianist Randy Newman, basketball player Michael Cooper, tennis player Darlene Hard, composer John Cage, musician James Hetfield, science fiction writer Larry Niven and sculptor Isamu Nochu i.
